Kinship links ap human geography delve into the intricate web of familial relationships that shape human societies. Kinship systems, varying from patrilineal to matrilineal, profoundly impact social organization, cultural identity, economic systems, political structures, and migration patterns. Understanding these kinship links is essential for unraveling the complexities of human geography.
Kinship ties extend beyond biological connections, encompassing cultural and emotional bonds that define belonging and shape values. They influence inheritance patterns, resource allocation, and political power dynamics. Moreover, kinship networks provide support and resources for migrants, facilitating their integration into new environments.
Kinship Links and Family Structures
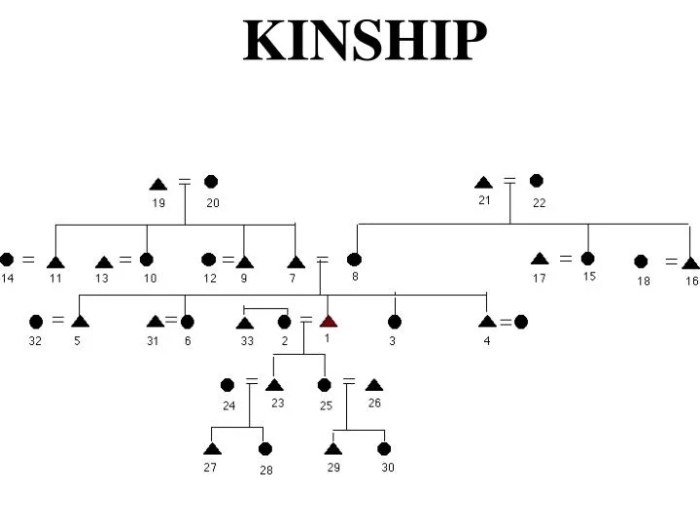
Kinship links refer to the social ties that connect individuals based on blood, marriage, or adoption. These links play a crucial role in human geography, shaping family structures, social networks, and community organization.
Types of Kinship Systems
Kinship systems vary across cultures, influencing how individuals are related to one another and how families are structured. Three primary types of kinship systems exist:
- Patrilineal:Kinship is traced through the father’s line, with children inheriting their father’s clan or lineage.
- Matrilineal:Kinship is traced through the mother’s line, with children inheriting their mother’s clan or lineage.
- Bilateral:Kinship is traced through both the father’s and mother’s lines, with children inheriting from both sides.
These systems impact inheritance patterns, property rights, and social obligations within families and communities.
Impact on Family Structures
Kinship links shape family structures by determining who is considered a family member and how they are related. In patrilineal societies, for example, extended families often consist of a man, his wife, his unmarried children, and his married sons and their families.
In matrilineal societies, extended families may include a woman, her husband, her unmarried children, and her married daughters and their families.
Social Networks and Community Organization
Kinship links also influence social networks and community organization. Individuals who share kinship ties often form close social bonds and provide mutual support. In some cultures, kinship networks serve as the basis for social organization, with communities structured around extended families or clans.
Kinship and Cultural Identity
Kinship links play a pivotal role in shaping cultural identity and fostering a sense of belonging within a society. They establish a network of familial relationships that provide individuals with a sense of connectedness, shared values, and traditions.
Values, Norms, and Traditions
Kinship ties influence the development of values, norms, and traditions within a society. Extended families often share a common set of beliefs, practices, and expectations that are passed down through generations. These shared values and norms shape individual behavior and contribute to the collective identity of the group.
For example, in many collectivist societies, the extended family is highly valued, and individuals are expected to prioritize the needs of their kin over their own. This emphasis on family loyalty and interdependence reinforces the importance of kinship links in shaping cultural identity.
Cultural Practices
The importance of kinship links is often reflected in cultural practices and rituals. Many societies have specific ceremonies or events that celebrate family relationships, such as weddings, funerals, and family reunions. These events provide opportunities for extended families to come together, strengthen their bonds, and pass on cultural traditions.
For instance, in some African cultures, traditional marriage ceremonies involve the participation of extended family members from both sides. These ceremonies not only celebrate the union of two individuals but also reinforce the importance of kinship ties and the continuity of the family lineage.
Kinship and Economic Systems
Kinship links play a significant role in shaping economic organization and resource allocation within different societies. Kinship networks provide a framework for cooperation, support, and exchange, influencing access to resources, labor division, and inheritance patterns.
Kinship and Access to Resources
In many traditional societies, kinship ties determine access to land, water, and other natural resources. For example, in some pastoralist societies, grazing rights are allocated based on lineage affiliation. In agricultural communities, land inheritance laws may favor certain kinship groups, such as the eldest son or the male lineage.
Kinship and Labor Division
Kinship networks also influence labor division within families and communities. In societies with strong kinship bonds, tasks and responsibilities are often allocated along kinship lines. For instance, in extended family households, younger members may assist with childcare or agricultural labor, while older members provide guidance and support.
Kinship and Inheritance Patterns, Kinship links ap human geography
Kinship links shape inheritance patterns, determining who inherits property, wealth, and other assets. In some societies, inheritance is governed by primogeniture, where the eldest child inherits the majority of the estate. In others, inheritance is divided equally among all children, regardless of gender or age.
Kinship ties can also influence the distribution of wealth within extended families or clans.
Kinship Networks and Economic Activities
Kinship networks facilitate various economic activities and support livelihoods. In rural communities, extended families often work together in agricultural production, sharing resources and labor. In urban areas, kinship ties can provide access to employment opportunities, housing, and financial assistance.
Examples of Kinship-Based Economic Activities
- Family-owned businesses and farms
- Cooperative labor arrangements among kin groups
- Exchange of goods and services within extended families
- Inheritance-based wealth accumulation
- Access to land and other resources through kinship connections
Kinship and Political Systems

Kinship links play a pivotal role in shaping political organization, influencing leadership roles, decision-making processes, and social hierarchies. In societies where kinship ties are strong, political power and authority are often concentrated within specific lineages or clans.
Leadership Roles: Kinship often determines who can assume leadership positions. In patrilineal societies, leadership is typically passed down from father to son, while in matrilineal societies, it is passed down through the female line. In some cases, specific clans or lineages may have exclusive rights to hold certain political offices.
Decision-Making Processes: Kinship ties can also influence decision-making processes within political systems. In societies with strong kinship bonds, important decisions may be made through consensus among family members or clan elders. Kinship networks can also serve as channels for information exchange and the mobilization of support for political decisions.
Social Hierarchies: Kinship links can contribute to the formation of social hierarchies. In societies where kinship is closely tied to social status, individuals born into certain lineages or clans may have higher social standing and access to political power.
Examples
- In many African societies, kinship plays a central role in political organization. In the Ashanti kingdom of Ghana, for example, the Asantehene (king) is chosen from a specific royal lineage, and his authority is supported by a network of kinship ties.
- In some parts of India, caste systems based on kinship and lineage determine political power and social status. Individuals born into higher castes have greater access to political office and decision-making.
- In feudal societies, kinship ties were often used to establish and maintain political alliances. Marriages between royal families were common, and kinship networks played a crucial role in securing political stability and expanding territories.
Kinship and Migration
Kinship links play a significant role in shaping migration patterns and settlement choices. Migrants often rely on their kinship networks for support and resources in new environments.
Kinship networks provide migrants with emotional and financial support, as well as access to information and resources. They help migrants to find housing, jobs, and healthcare, and they can also provide social and cultural support.
Kinship Ties and Migrant Communities
Kinship ties often shape the formation and structure of migrant communities. Migrants from the same region or village often settle in the same area, forming enclaves or ethnic neighborhoods. These communities provide a sense of belonging and support for migrants, and they can help to preserve their cultural identity.
- In the United States, for example, Mexican immigrants often settle in barrios, which are neighborhoods that are home to a large Mexican population. These barrios provide migrants with a sense of community and support, and they help to preserve Mexican culture.
- Similarly, in Europe, Turkish immigrants often settle in enclaves, which are neighborhoods that are home to a large Turkish population. These enclaves provide migrants with a sense of community and support, and they help to preserve Turkish culture.
Kinship and Integration Processes
Kinship ties can also influence integration processes. Migrants who have strong kinship ties to their home country may be less likely to integrate into their new society. They may maintain close ties to their home country, and they may not adopt the language or customs of their new country.
- For example, a study of Mexican immigrants in the United States found that those who had strong kinship ties to Mexico were less likely to learn English and more likely to return to Mexico.
- However, kinship ties can also facilitate integration. Migrants who have kinship ties to both their home country and their new country may be more likely to integrate successfully. They can serve as bridges between the two cultures, and they can help to build understanding and cooperation.
Question & Answer Hub: Kinship Links Ap Human Geography
What is the significance of kinship links in human geography?
Kinship links are the fundamental building blocks of human societies, shaping social organization, cultural identity, economic systems, political structures, and migration patterns.
How do different kinship systems impact social organization?
Kinship systems, such as patrilineal, matrilineal, and bilateral, determine inheritance patterns, resource allocation, and social hierarchies, thereby influencing the organization of societies.
What is the role of kinship links in shaping cultural identity?
Kinship ties provide a sense of belonging and shape values, norms, and traditions within societies. They influence cultural practices and rituals that reinforce kinship bonds.
How do kinship networks facilitate economic activities?
Kinship networks provide access to resources, labor, and support, enabling individuals to engage in economic activities and secure livelihoods.
What is the impact of kinship links on migration patterns?
Kinship networks provide support and resources for migrants, influencing their migration decisions, settlement choices, and integration processes in new environments.