Lab 10-3 configure system logging – Lab 10-3: Configure System Logging introduces the fundamental concepts and techniques of system logging in network management, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance, configuration, and analysis. This in-depth exploration empowers network administrators with the knowledge and skills to effectively manage and utilize system logs for enhanced network performance, security, and troubleshooting.
System Logging Configuration: Lab 10-3 Configure System Logging
System logging plays a crucial role in network management, providing a detailed record of system events, activities, and errors. By configuring system logging effectively, network administrators can monitor the health and performance of their networks, troubleshoot issues promptly, and maintain a secure environment.
Step-by-Step Guide to Configure System Logging
- Identify the logging facility and severity levels to be used.
- Configure the logging destination (e.g., file, syslog server).
- Specify the format and content of the log messages.
- Enable logging for the desired services and applications.
- Test and verify the logging configuration.
Types of Log Files and Their Purposes
- System Log:Records system events, such as boot, shutdown, and hardware changes.
- Application Log:Captures events and errors related to specific applications.
- Security Log:Tracks security-related events, such as login attempts, failed connections, and intrusion attempts.
- Network Log:Records network-related events, such as connection attempts, packet drops, and routing changes.
Log Analysis and Monitoring
Log analysis and monitoring are essential for maintaining a secure and efficient network. By analyzing log files, administrators can identify potential issues, track user activity, and detect security breaches.
Importance of Log Analysis, Lab 10-3 configure system logging
- Troubleshooting network issues
- Security monitoring and threat detection
- Performance optimization
- Compliance and auditing
Techniques for Log Analysis
- Use log analysis tools (e.g., grep, awk, sed).
- Correlate log entries from different sources.
- Establish baselines and monitor for anomalies.
- Automate log analysis using scripts or SIEM tools.
Log Management Best Practices
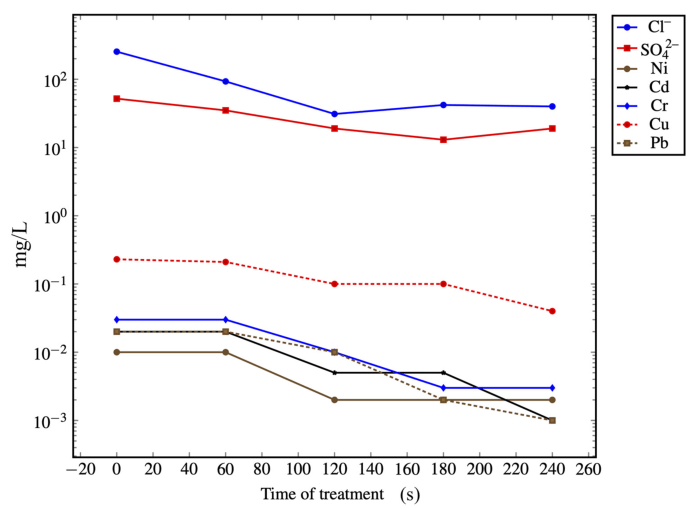
Effective log management practices ensure that log files are properly managed, stored, and protected.
Rotation, Retention, and Backup Strategies
- Rotate log files regularly to prevent them from becoming too large.
- Retain log files for a predefined period to comply with regulations and for troubleshooting purposes.
- Backup log files regularly to prevent data loss in case of system failure.
Centralized Log Management Systems
- Provide a centralized repository for all log files.
- Simplify log analysis and monitoring.
- Enhance security by centralizing access control and data protection.
Security Considerations
- Control access to log files to prevent unauthorized modifications.
- Encrypt log files to protect sensitive information.
- Monitor log files for suspicious activities.
Troubleshooting with System Logs
System logs provide valuable insights into network issues and can assist in troubleshooting.
Using System Logs for Troubleshooting
- Identify error messages and warnings.
- Correlate log entries from different sources.
- Search for patterns and trends in the log files.
- Use log analysis tools to filter and analyze log entries.
Importance of Log Correlation
Correlating log entries from different sources provides a comprehensive view of system events and helps identify the root cause of issues.
Advanced Logging Techniques
Advanced logging techniques extend the capabilities of system logging and provide additional insights into network activity.
Syslog
- A standardized protocol for sending log messages to a central server.
- Provides a flexible and scalable way to manage log files.
SNMP Traps
- Notifications sent by network devices when specific events occur.
- Provide real-time alerts for critical events.
Event Forwarding
- The process of sending log messages to a third-party system for analysis and storage.
- Enhances log management and security by integrating with SIEM tools.
Query Resolution
What is the primary purpose of system logging in network management?
System logging provides a detailed record of events and activities occurring within a network, facilitating troubleshooting, security monitoring, and performance analysis.
What are the key steps involved in configuring system logging?
Configuring system logging typically involves selecting the appropriate log level, specifying the log file location, and defining log rotation and retention policies.
How can log analysis assist in troubleshooting network issues?
Log analysis enables administrators to identify patterns, errors, and anomalies within system logs, providing valuable insights into the root causes of network problems.