Nuclear physics webquest answer key – Welcome to the fascinating realm of nuclear physics, where we delve into the mysteries of the atom’s nucleus. This comprehensive webquest answer key serves as your guide to unlocking the secrets of nuclear physics, providing a clear and concise explanation of its fundamental concepts, reactions, applications, and ethical considerations.
Through a captivating exploration of nuclear physics, we will unravel the structure of atoms, witness the dynamics of nuclear reactions, and examine the profound impact of nuclear physics on medicine, energy production, and military technology.
Nuclear Physics Concepts
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies the structure, properties, and interactions of atomic nuclei. The nucleus is the central part of an atom, and it contains protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons have no charge.
The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element of the atom. For example, all atoms with one proton are hydrogen atoms.The nucleus is held together by the strong nuclear force, which is one of the four fundamental forces of nature.
The strong nuclear force is much stronger than the electromagnetic force, which is responsible for the interactions between charged particles. This is why the nucleus is so stable, even though it contains positively charged protons that would otherwise repel each other.The
structure of the nucleus is complex, and it is still not fully understood. However, scientists have made great progress in understanding the nucleus over the past century. In the early 20th century, Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus by bombarding gold atoms with alpha particles.
In the 1930s, James Chadwick discovered the neutron. In the 1950s, Maria Goeppert Mayer and J. Hans D. Jensen developed the nuclear shell model, which explains the structure of the nucleus in terms of energy levels.
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. For example, carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14 are all isotopes of carbon. Carbon-12 has six protons and six neutrons, carbon-13 has six protons and seven neutrons, and carbon-14 has six protons and eight neutrons.Isotopes
have different properties because they have different masses. For example, carbon-12 is the most common isotope of carbon, and it has a mass of 12 atomic mass units (amu). Carbon-13 has a mass of 13 amu, and carbon-14 has a mass of 14 amu.
The different masses of isotopes can affect their chemical and physical properties. For example, carbon-14 is radioactive, while carbon-12 and carbon-13 are not.
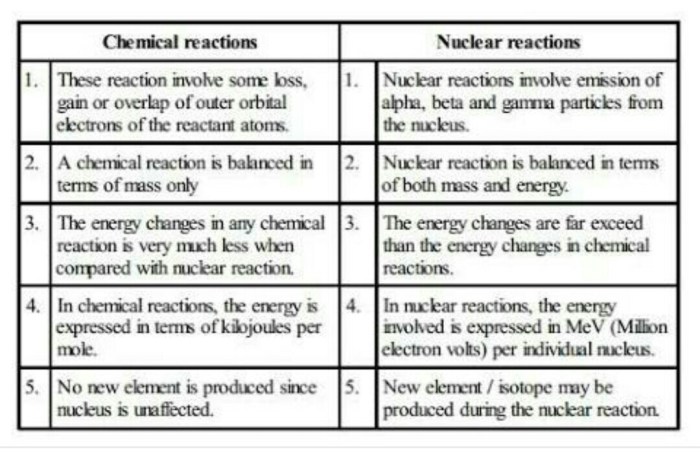
Nuclear Reactions
Nuclear reactions are processes that change the structure of atomic nuclei. Nuclear reactions can be either spontaneous or induced. Spontaneous nuclear reactions occur naturally, while induced nuclear reactions are caused by the interaction of a nucleus with an external particle, such as a neutron or a proton.There
are many different types of nuclear reactions, but the most common are nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. Nuclear fission is the process of splitting a heavy nucleus into two or more lighter nuclei. Nuclear fusion is the process of combining two or more light nuclei into a heavier nucleus.Nuclear
reactions can release large amounts of energy. This energy can be used to generate electricity or to power weapons. Nuclear reactions are also used in a variety of medical applications, such as cancer treatment.
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is the process of splitting a heavy nucleus into two or more lighter nuclei. Nuclear fission is a chain reaction, which means that it can continue on its own once it has started. This is because the neutrons that are released when a nucleus fissions can go on to fission other nuclei.Nuclear
fission is used to generate electricity in nuclear power plants. In a nuclear power plant, uranium-235 is used as the fuel. Uranium-235 is a heavy nucleus that is easily fissioned by neutrons. When a neutron strikes a uranium-235 nucleus, the nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei, releasing two or three neutrons.
These neutrons can then go on to fission other uranium-235 nuclei, creating a chain reaction. The energy released by the chain reaction is used to heat water, which turns into steam and drives a turbine that generates electricity.
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is the process of combining two or more light nuclei into a heavier nucleus. Nuclear fusion is the opposite of nuclear fission. Nuclear fusion is a very difficult process to achieve, but it releases much more energy than nuclear fission.
This is because the mass of the products of a nuclear fusion reaction is less than the mass of the reactants. The difference in mass is converted into energy according to Einstein’s equation E=mc^2.Nuclear fusion is the process that powers the sun and other stars.
In the sun, hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium nuclei. This process releases the energy that keeps the sun shining.Scientists are working on developing nuclear fusion as a source of energy for Earth. Nuclear fusion has the potential to provide a clean, safe, and sustainable source of energy.
However, there are still many challenges that need to be overcome before nuclear fusion can be used to generate electricity on a commercial scale.
Applications of Nuclear Physics
Nuclear physics has a wide range of applications in medicine, energy production, and military technology.
Medical Applications, Nuclear physics webquest answer key
Nuclear physics is used in a variety of medical applications, such as cancer treatment. Radiation therapy is a common treatment for cancer. Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be used to treat a variety of cancers, including breast cancer, lung cancer, and prostate cancer.Nuclear
medicine is another medical application of nuclear physics. Nuclear medicine uses radioactive isotopes to diagnose and treat diseases. For example, radioactive iodine can be used to diagnose and treat thyroid cancer.
Energy Production
Nuclear power is a major source of electricity around the world. Nuclear power plants use nuclear fission to generate electricity. Nuclear power is a clean and efficient source of energy, but it also produces radioactive waste. Radioactive waste must be disposed of safely and securely.Nuclear
fusion is a promising new source of energy. Nuclear fusion does not produce radioactive waste, and it is a much more efficient source of energy than nuclear fission. However, nuclear fusion is still in the early stages of development.
Military Technology
Nuclear weapons are the most powerful weapons ever created. Nuclear weapons use nuclear fission or nuclear fusion to release massive amounts of energy. Nuclear weapons have been used in war only twice, in the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.The
development of nuclear weapons has had a profound impact on international relations. The threat of nuclear war has led to the development of arms control treaties and other measures to prevent nuclear proliferation.
Safety and Ethics in Nuclear Physics
Nuclear physics is a powerful technology that can be used for good or for evil. It is important to use nuclear physics safely and ethically.
Safety
There are a number of safety measures that must be taken when handling radioactive materials. These measures include:* Using proper shielding to protect workers from radiation exposure
- Storing radioactive materials in secure locations
- Disposing of radioactive waste safely and securely
Ethics
There are also a number of ethical considerations related to nuclear physics. These considerations include:* The use of nuclear weapons
- The disposal of nuclear waste
- The proliferation of nuclear weapons
It is important to weigh the benefits and risks of nuclear physics carefully before making decisions about how to use this technology.
Nuclear Accidents
There have been a number of nuclear accidents throughout history. The most serious nuclear accident was the Chernobyl disaster in 1986. The Chernobyl disaster occurred when a nuclear reactor exploded, releasing large amounts of radioactive material into the environment. The Chernobyl disaster had a devastating impact on the local population and the environment.Other
notable nuclear accidents include the Three Mile Island accident in 1979 and the Fukushima Daiichi accident in 2011. The Three Mile Island accident was a partial meltdown of a nuclear reactor, while the Fukushima Daiichi accident was a complete meltdown of three nuclear reactors.
Both accidents released significant amounts of radioactive material into the environment.Nuclear accidents are a reminder of the importance of safety and ethics in nuclear physics. It is important to take all necessary precautions to prevent nuclear accidents from happening.
Commonly Asked Questions: Nuclear Physics Webquest Answer Key
What is the basic principle of nuclear physics?
Nuclear physics focuses on the study of the nucleus of an atom, including its structure, composition, and behavior.
What are the different types of nuclear reactions?
Nuclear reactions encompass a range of processes, including nuclear fission, nuclear fusion, and radioactive decay.
How is nuclear physics applied in medicine?
Medical applications of nuclear physics include cancer treatment through radiation therapy and diagnostic imaging techniques.