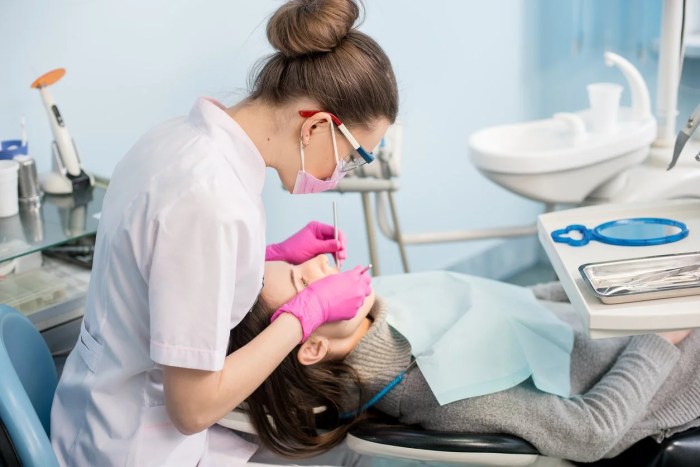
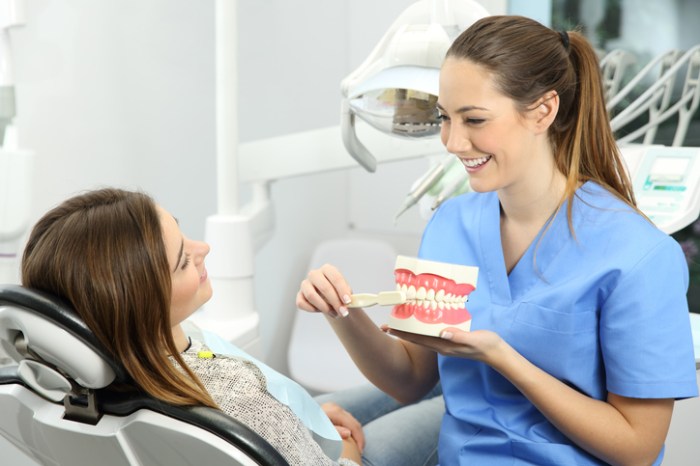
The clinical practice of dental hygienists plays a pivotal role in maintaining optimal oral health and preventing dental diseases. These healthcare professionals are highly skilled and knowledgeable, providing a wide range of preventive, therapeutic, and educational services to patients of all ages.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted aspects of dental hygiene practice, exploring the scope of practice, patient assessment and diagnosis, treatment planning and implementation, patient education and counseling, collaboration and interdisciplinary care, technology and innovation, research and evidence-based practice, continuing education and professional development, and ethical and legal considerations.
Introduction: Clinical Practice Of Dental Hygienist
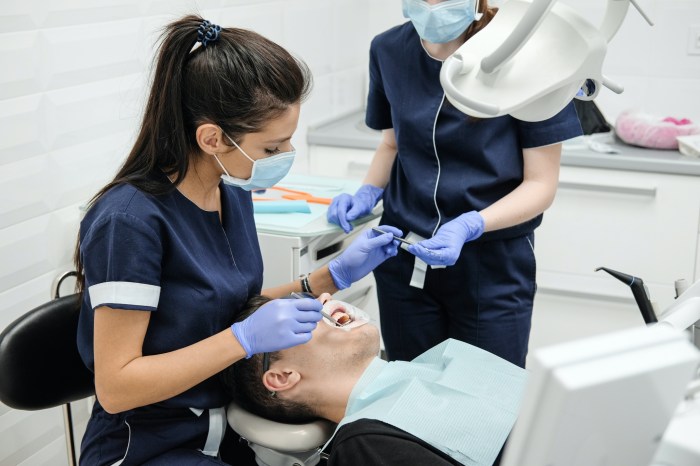
Dental hygiene is a licensed health care profession that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of oral diseases and conditions. Dental hygienists play a vital role in maintaining and improving the oral health of individuals and communities.
In a clinical setting, dental hygienists perform a wide range of procedures and techniques, including:
- Conducting oral health assessments
- Scaling and root planing
- Applying fluoride treatments
- Placing sealants
- Providing patient education and counseling
Dental hygienists work closely with dentists and other dental professionals to provide comprehensive oral health care.
Scope of Practice, Clinical practice of dental hygienist
The scope of practice for dental hygienists varies depending on state or regional regulations. In general, dental hygienists are authorized to perform the following procedures:
- Take and record vital signs
- Obtain and interpret dental radiographs
- Perform oral cancer screenings
- Administer local anesthesia
- Place and remove temporary restorations
- Apply fluoride treatments
- Provide patient education and counseling
Dental hygienists must practice within the legal and ethical boundaries of their profession. They must obtain informed consent from patients before performing any procedures and maintain patient confidentiality.
Patient Assessment and Diagnosis
Dental hygienists play a crucial role in assessing patients’ oral health status and diagnosing common oral diseases and conditions. The assessment process typically involves:
- Medical and dental history review
- Oral examination
- Radiographic examination
Based on the assessment findings, dental hygienists use established criteria to diagnose common oral diseases and conditions, such as:
- Dental caries
- Periodontal disease
- Oral cancer
Treatment Planning and Implementation
Dental hygienists collaborate with dentists to develop personalized treatment plans for patients based on their individual needs and diagnosis. The treatment plan may include:
- Scaling and root planing
- Fluoride treatments
- Sealant placement
- Patient education and counseling
Dental hygienists perform scaling and root planing to remove plaque and calculus from the teeth and root surfaces. Fluoride treatments help strengthen teeth and prevent tooth decay. Sealants are applied to the chewing surfaces of teeth to protect them from decay.
Patient education and counseling are essential components of any treatment plan, as they help patients understand their oral health status and how to maintain good oral hygiene.
Patient Education and Counseling
Patient education and counseling are vital aspects of dental hygiene practice. Dental hygienists play a key role in educating patients about:
- Proper oral hygiene techniques
- Disease prevention strategies
- Treatment options
Effective communication techniques are essential for patient education and counseling. Dental hygienists use clear and concise language, avoid jargon, and encourage patient questions and feedback.
Popular Questions
What are the primary responsibilities of a dental hygienist?
Dental hygienists perform a variety of tasks, including conducting oral health assessments, cleaning teeth, removing plaque and tartar, applying fluoride treatments, taking dental X-rays, and providing patient education on oral hygiene practices.
What is the scope of practice for dental hygienists?
The scope of practice for dental hygienists varies depending on the state or country in which they practice. Generally, dental hygienists are authorized to perform preventive and therapeutic procedures under the supervision of a dentist.
How do dental hygienists contribute to interdisciplinary care?
Dental hygienists collaborate with dentists, periodontists, and other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive oral health care to patients. They share patient information, participate in treatment planning, and provide support during dental procedures.
What are the ethical principles that guide dental hygiene practice?
Dental hygienists are guided by ethical principles such as patient autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice. They respect patient confidentiality, obtain informed consent before performing procedures, and strive to provide the highest quality of care.


